Data management is the IT discipline focused on ingesting, preparing, organizing, processing, storing, maintaining, and securing data throughout the enterprise. Data management is typically the responsibility of a data architect or database administrator, and the goal is ensuring that the organization’s data is consistent, usable, and secure across all enterprise systems and applications. End-to-end data management is aspirational for most enterprises, but all businesses should have an intentional, overarching data management strategy in place to guide their work.
Table of Contents
How Does Data Management Work?
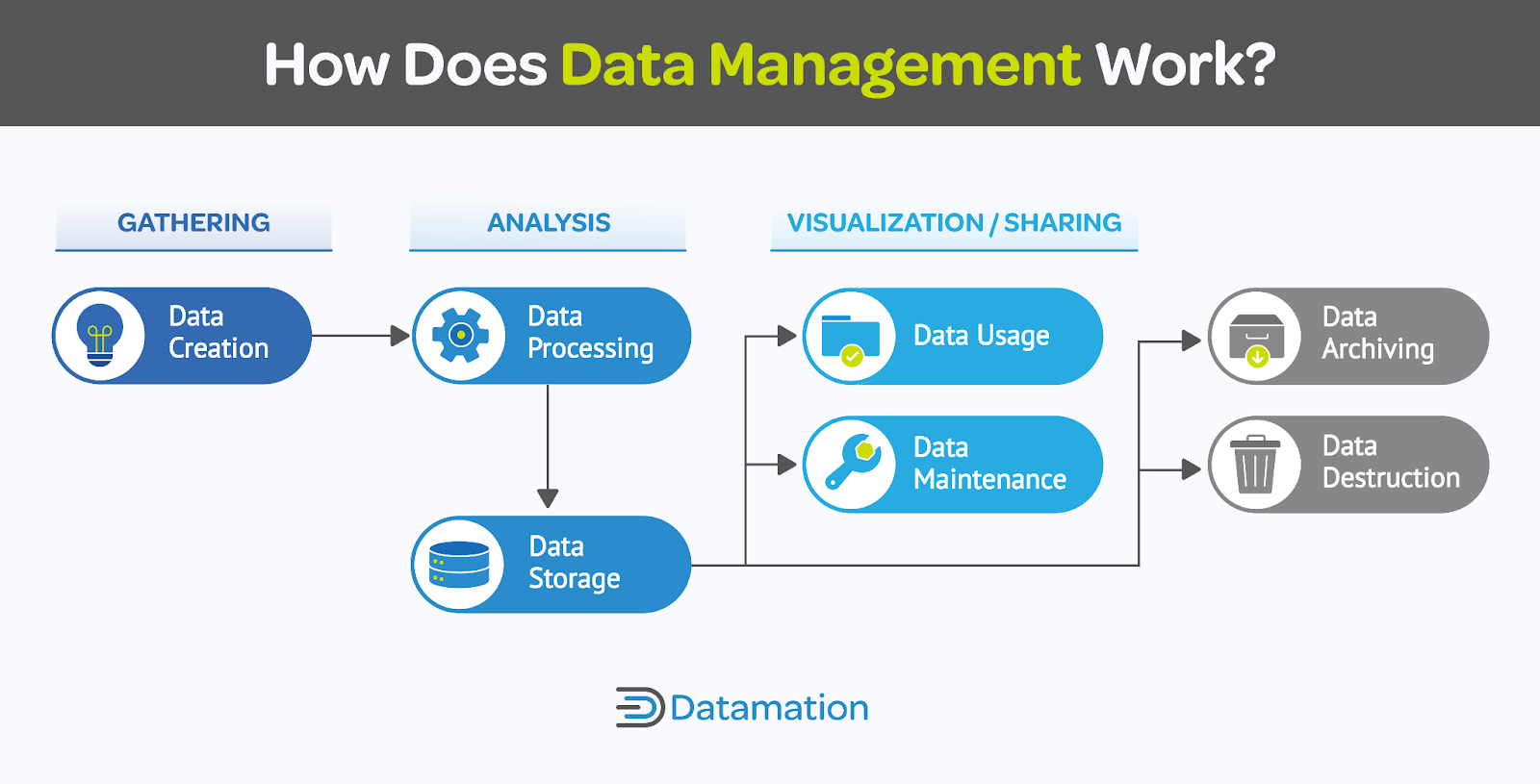
Effective data management is done using a host of software-based tools that render data consistent across all systems, ensure it is of highest quality, and ensure that it meets security and governance standards. While data management is generally the role of a data architect, it engages nearly every IT discipline.
For example, if a business contracts with outside cloud vendors, data management often falls to the IT application manager, an IT security unit, the database group, an IT vendor contract management group, or even outside users and auditors. It is their responsibility to ensure that the data being furnished by the vendors meets or exceeds the standards that enterprises set for themselves.
When new applications and systems access data from other systems, the application team generally works with the database team to ensure that all data is accessible and usable across all system boundaries. The IT storage group or network group might make decisions about where data is ultimately stored. In short, virtually the entire IT team is involved in data management at some point, with the data architect or data administrator giving direction.
7 Types of Data Management
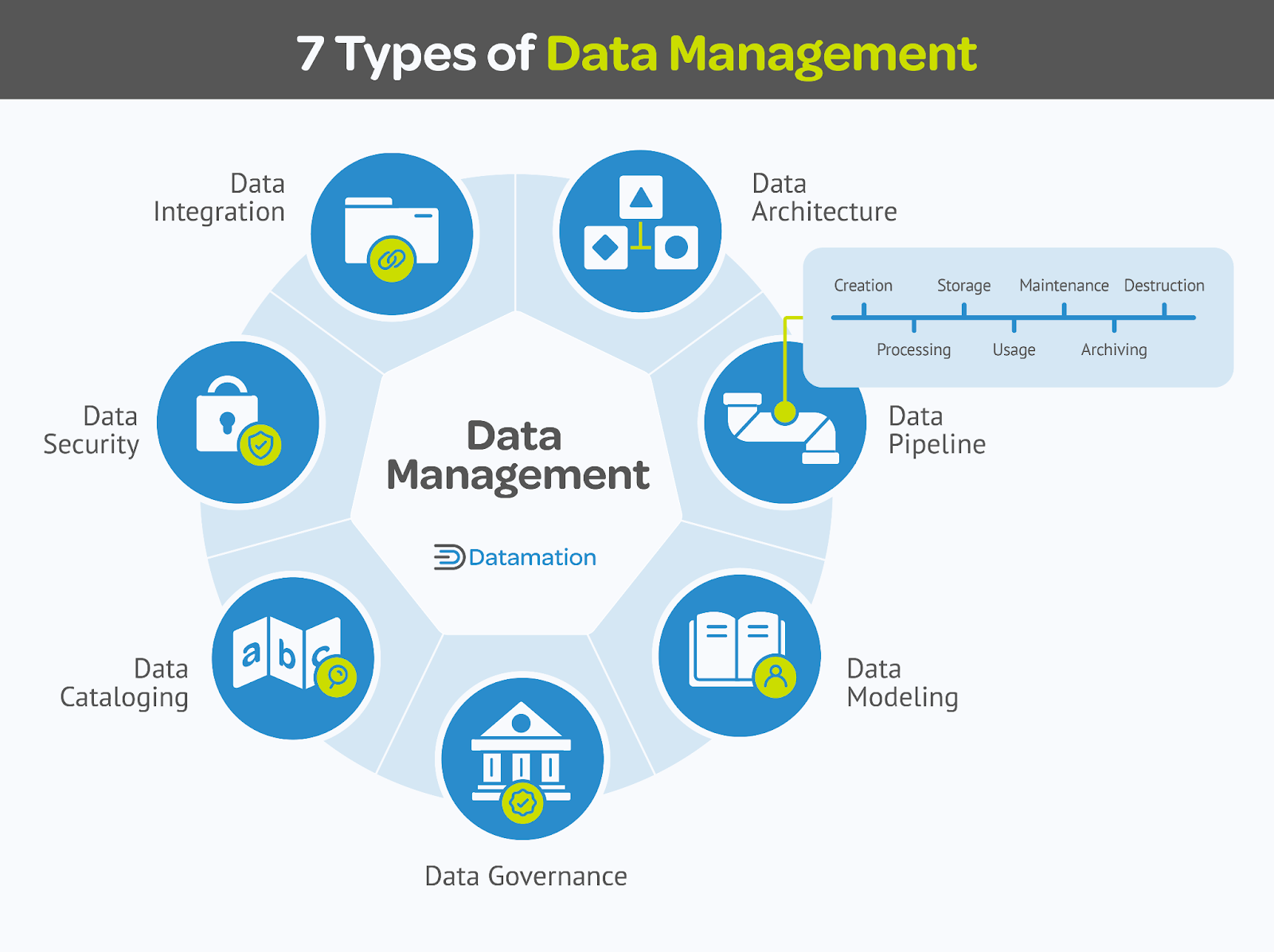
Organizations can employ different types of data management depending upon their unique datasets. While smaller businesses may use a few data management approaches, larger organizations may require a wider range of comprehensive techniques to best care for their data.
Data Architecture
Data architecture is a framework that helps an organization’s IT infrastructure with its data strategy by setting standards on how data is managed throughout its lifecycle. The ultimate goal is to ensure that data is high quality and reliable to inform strategic business decisions.
Data Modeling
Data modeling is a visual representation of an organization’s data, how it moves through the organization, and how it relates. The model sets rules for these relationships and determines how data moves according to those rules.
Data Pipelines
Data pipelines are automated workflows or pathways that allow data to get to their desired locations after it is processed. This enables a seamless extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data from various sources to target specific destinations such as data warehouses or analytics platforms.
Data Cataloging
A data catalog involves the comprehensive inventorying or categorizing of an organization’s data assets and encompasses important metadata such as data definitions, lineage, usage, and access controls. Data catalogs frequently include additional functions that expedite data exploration and facilitate personalized queries and optimize data use.
Data Integrations
Data integration is the process of combining data from various sources into a complete, accurate, and up-to-date dataset for analysis, reporting, and operational purposes. Specific data techniques such as data replication, synchronization, and API-based connections facilitate seamless data exchange and allow these data to operate collaboratively across platforms or departments within the organization.
Data Governance
Data governance is a set of rules, strategic frameworks, policies, and processes to assure data quality, security, and compliance of an organization’s data assets. Rules and responsibilities are involved to enforce data standards and controls; establishing mechanisms for data stewardship, monitoring, and enforcement, mitigates risks and maximizes the value of data sources.
Data Security
Data security protects digital information from unauthorized access, manipulation, or theft, and includes physical hardware security, administrative controls, software application security, and organizational policies. Encryption, data masking, and redaction procedures help guarantee compliance and defend against cyber assaults, insider risks, and human error.
8 Data Management Best Practices
Best data management practices are essential guidelines for how businesses handle data, transforming it into a strategic resource that can be used to drive development and innovation.
- Define Clear Data Management Goals: To create a clear and attainable data strategy, first identify data requirements and establish quantifiable targets consistent with corporate goals.
- Create a Data Governance Framework: Data governance entails creating roles, responsibilities, and procedures to guarantee that data follows corporate rules and standards.
- Ensure Data Quality Assurance: Data quality assurance is the process of ensuring correctness and dependability through validation, cleaning, and normalization to keep data error-free and consistent.
- Ensure Data Security and Privacy: Encryption, access limits, and regular security audits are all necessary for protecting sensitive data, confidentiality, and integrity, and avoiding unwanted access or cyber threats.
- Streamline Data Integrations: This entails developing effective techniques for merging data from several sources to offer a complete and cohesive perspective and improve data usability.
- Enforce Documentation and Metadata Management: Keeping thorough records of data sources, structures, and metadata is critical for comprehending and managing data; it promotes traceability and helps to preserve the organization’s knowledge base
- Enforce Data Lifecycle Management: Managing the flow of data from creation to retirement ensures that it is relevant, accessible, and safe throughout its lifespan; this approach includes implementing procedures for data preservation, archiving, and disposal.
- Implement Master Data Management: Master Data Management (MDM) establishes a single source of truth for key corporate data, assuring consistency and correctness across all systems and divisions within an organization.
9 Benefits of Data Management
Data management can greatly improve an organization’s performance and decision-making ability. Here are some of the most common benefits:
- Eliminates Data Redundancy: By combining data sources and adopting a single source of truth, data management decreases data duplication across systems, resulting in more effective storage and retrieval processes.
- Improves Data Sharing: Effective data management promotes data exchange inside an organization and with external partners to foster teamwork and innovation.
- Strengthens Data Privacy and Security: Organizations may better safeguard sensitive data from breaches and unauthorized access by using strong data management procedures that ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
- Aids Backup and Recovery: Data management systems frequently feature automatic data backup and data recovery solutions, which are critical for ensuring business continuity in the event of a data loss or system failure.
- Streamlines Processes and Improves Efficiency: Data management may save time and improve operational efficiency by organizing and streamlining data operations, reducing redundancies, and automating repetitive tasks.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Proper data management enables firms to comply with legal and regulatory obligations by keeping correct records and applying essential controls.
- Improves Data Security: A well-managed data environment improves data security by safeguarding it from internal and external threats while also lowering the chance of data breaches.
- Enhances Business Performance: Organizations that use optimized data processes can improve their performance indicators, get insights into client preferences, and increase sales efficiency.
- Gives a Competitive Advantage: Companies may obtain a competitive edge in the market by exploiting high-quality, well-managed data, which allows them to respond more effectively to changes and client needs.
Notable Challenges of Data Management
Data management tools are readily available to help organizations manage various types of data that they collect. Even with these tools, some challenges are inevitable, including data overload, poor quality or insecure data, or data silos, but awareness of the obstacles can help keep you from being caught off guard.
Data Overload
The amount of data being generated can overwhelm organizations of all sizes. Organizations have to not just manage the influx of data, but process and analyze it for valuable insights. A comprehensive data strategy needs to encompass storage, processing, analysis, and security to keep businesses from being drowned by the abundance of data.
Data Quality
The term “garbage in, garbage out” applies to data management—poor quality data can affect the foundation of the decision-making process, leading to missed opportunities. Organizations must have routine data cleaning protocols and quality checks at every step of the data lifecycle to ensure that data remains accurate, consistent, and reliable.
Data Security
Poorly managed data can lead to breaches. Safeguarding sensitive information must be non-negotiable, and a proactive approach to data security must rely upon a multi-layered defense strategy that includes protocols such as vigilant data monitoring and rapid response.
Data Silos
Data collected from multiple sources can create a challenge for different team members to access if it’s not well organized and properly managed. It can be difficult to find the right solution for storing large amounts of data where it can be accessible and used. The best way to make data accessible is to use cloud storage and have an effective cloud-now storage strategy that lets companies store data and use AI/ML for faster data analysis, visualization, and data-driven decision-making.
Data Compliance
Going through the complex landscape of regulatory requirements is an ongoing challenge for any business. Since laws and regulations continuously evolve, maintaining data compliance can be a moving issue. Using automated compliance tools offers a proactive solution by regularly adapting to changing regulatory frameworks and ensuring continuous adherence to these evolving laws and regulations.
Lack of Skilled Workers
The demand for experienced data managers hinders organizations from fully optimizing their data management. Even though there are tools available to manage data, the shortage of experienced data management specialists capable of managing the entire process hinders an organization from maximizing the entire advantage of its data. Investing in entry-level data managers and providing them with tailored training may cost more but this can help an organization in having a streamline in processing their data.
Bottom Line: Company Strategies Should Evolve With Data Management
Organizations struggle to handle massive amounts of data efficiently in this fast-paced world of data management. Staying ahead requires continuous strategy development to adapt to this constant change, and investing in data management specialists helps organizations gain the competence they need to efficiently navigate the complex data environment. Embracing and adapting to these constant changes and technologies maximizes data utilization, streamlines operations, and improves the decision-making process. Adopting innovative and agile data management practices positions organizations to succeed in an increasingly data-driven world.
If you’re interested in data management, read about the types and challenges of data management, or see our expert picks for the top data management platforms and solutions.


