Data-driven decision-making is an approach that emphasizes using data and analysis instead of intuition to inform business decisions. It involves leveraging such data sources as customer feedback, market trends, and financial data to guide decision-making processes.
To completely embrace data-driven decision-making, organizations need to establish a culture that promotes critical thinking and curiosity at all levels to make decisions based on evidence and insights derived from comprehensive data analysis. The goal is to encourage all employees to question and investigate information, leading to the discovery of valuable insights that drive action.
When your business fully practices data-driven decision-making, all choices are supported by credible data and the probability of similar events recurring, leading to faster, more accurate, cost-effective decisions and eliminating bias and second-guessing.
Table of Contents
6 Key Steps of Data-Driven Decision-Making
The data-driven decision-making (DDDM) process involves six key steps: defining objectives, identifying and collecting data aligned with those objectives, organizing and exploring data, performing analysis on that data, drawing conclusions about what it says, and implementing and evaluating a plan based on those conclusions. As your organization increasingly relies on data to inform business strategies, mastering these steps can help you make well-informed choices.
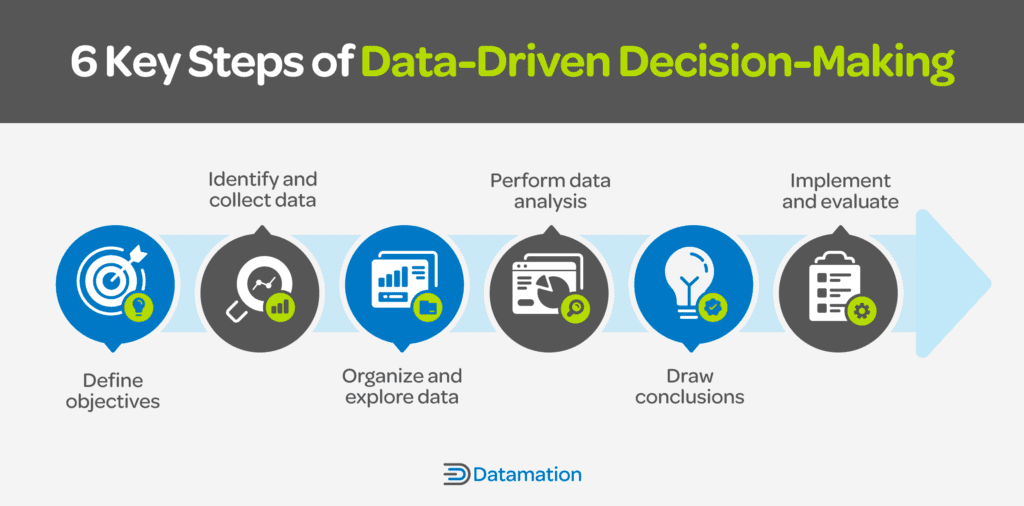
1. Define Objectives
Begin by gaining a thorough understanding and articulating your company’s vision and goals. Define specific problems or decisions that require attention using data-driven insights. This sets the stage for a focused and effective approach tailored to your organizational needs.
2. Identify and Collect Data
Survey your business teams to unveil areas and data sources aligned with your objectives. Use appropriate tools to systematically collect necessary data, making sure you are well-equipped for insightful analysis that caters to your needs.
3. Organize and Explore Data
Organize your enterprise data for effective visualization and exploration. Structure it to create a foundation for seamless exploration for a deeper understanding of relevant information tailored to your specific context.
4. Perform Data Analysis
Analyze the data using reporting tools and analytical methods to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations and extract actionable insights for your decision-making. Transform raw data into meaningful ones for informed choices that match your organizational goals.
5. Draw Conclusions
Draw clear conclusions from your data analysis and communicate the implications effectively by creating a narrative around the data for shared understanding within your team. Aim to make data accessible and impactful.
6. Implement and Evaluate
Develop and deploy a plan based on your drawn conclusions. Monitor the impact and effectiveness of this plan on your defined objectives. Through iterative evaluation, refine strategies for continuous improvement.
Data-Driven Decision-Making Examples
While DDDM is widely used across industries and sectors with a wide range of applications, here’s a look at a few real-world examples of how businesses, healthcare institutions, and educational organizations are using data to back their decisions and enhance their operations.
Data-Driven Decision-Making In Business
Different types of businesses use data for targeted marketing, inventory management, personalized recommendations, and preventing customer churn:
- Amazon: Uses data to segment customers based on location, demographics, and buying behavior to build targeted marketing campaigns.
- Walmart: Uses historical data and predictive analytics to strategically place holiday items across stores, optimizing the entire shopping experience.
- Netflix: Uses data for customized suggestions, minimizing customer churn and boosting retention rates.
Data-Driven Decision-Making In Education
Educational institutions use data for analysis to gauge performance, catch warning signs of failing students, and develop curriculum:
- Purdue University: Uses a predictive analytics tool called Course Signals to monitor performance and predict students at risk of not successfully completing a course.
- Indiana University: Uses data analytics to make sure course offerings match student demand.
Data-Driven Decision-Making In Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use data to refine patient care, prevent diseases, and conduct research:
- Cleveland Clinic: Leverages data to examine the impact of factors outside of the health system on a patient’s health. It also uses analytics to identify patients that would recover successfully at home following surgery.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Uses data to build informed decisions and establish systems for emergency operations and response.
- The Broad Institute: Uses big data analytics to advance drug discovery.
5 Benefits of Data-Driven Decision-Making
Businesses can transform their operations and position themselves for long-term success by adopting a data-driven decision-making model, improving the experience for their customers and cutting-costs in the process.
Improved Customer Experience
Data-driven enterprises are more customer-focused and gain a deeper understanding of customer journeys. DDDM elevates customer experience by giving insights into customer behavior and needs. It helps you tailor your business offerings, improve services, and address customer issues effectively. This leads to personalized experiences, stronger customer relationships, and higher revenue.
Better Strategic Planning
By using data to inform our choices, we can set achievable goals and stay ahead of the competition. DDDM promotes collaboration by creating a common understanding across departments, supporting communication, and encouraging a shared commitment to achieving organizational goals.
Growth Opportunities
DDDM enables you to identify new business opportunities and areas for improvement. It helps uncover trends and patterns for spotting new market opportunities. It also lets your business swiftly uncover bottlenecks and areas you need to work on.
Increased Operational Efficiency and Optimized Costs
Relying on data can uncover productivity bottlenecks and optimize resource use, resulting in better business efficiency. Furthermore, it facilitates accurate demand forecasting, leading to significant cost savings.
More Accurate Forecasting
Since data-driven decisions allow for more accurate forecasts and predictions about the future, it brings about more efficient operations and cost reductions. For instance, AI-driven forecasting in supply chain management can reduce errors, translating into a decrease in lost sales.
5 Pro Tips For Making Data-Driven Decisions
Harnessing the power of data can lead to more informed decisions, driving enterprise success. Here are some pro tips to help you make effective, data-driven decisions, emphasizing the importance of clarity, accuracy, culture, context, and continuous improvement:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define your business objectives before diving into data analysis. Understanding what you want to achieve helps in finding the relevant data to analyze and guarantees that your decisions are aligned with strategic goals.
- Prioritize Accuracy and Reliability: Inaccurate or unreliable data can lead to flawed insights and misguided decisions, so make sure that your data sources are accurate and updated. In addition, conduct regular data validation and cleansing to ensure data quality.
- Combine Data with Context: While data provides valuable insights, it’s crucial to combine it with a contextual understanding of your business environment to gain a holistic approach to decision-making. Consider industry trends, market dynamics, and qualitative factors.
- Promote a Data-Driven Culture: Foster a culture within your organization that encourages and values data-driven decision-making. This means offering training and resources for employees to enrich their data literacy, making data accessible, and promoting the use of data in discussions and decision processes.
- Iterate and Learn from Insights: Think of data-driven decision-making as a learning journey. Keep reviewing and adjusting your strategies based on what you learn and changes in the situation. Don’t just celebrate successes, but also learn from failures to keep improving your approach.
Common Challenges and Misconceptions about Data-Driven Decision-Making
Businesses in many industries turn to data-driven decision-making for precision and efficiency. However, the journey to harnessing data’s full potential isn’t without its challenges and misconceptions. Navigating these hurdles calls for a keen understanding of the common pitfalls associated with data-driven approaches.

Neglecting Data Quality
When it comes to making decisions based on data, one of the challenges is checking the data’s quality. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate and unreliable insights, resulting in flawed decision-making. Good data management practices involve ensuring the quality of the data
A common misconception related to this is thinking that more data is always better, but the real trick is having high-quality, complete, and accurate data to make decisions you can trust. Having too much data— especially if it’s irrelevant or not properly analyzed—can overwhelm decision-makers and lead to information paralysis.
Scattered Data
Disorganized data scattered across different departments are like pieces of a puzzle that just won’t fit together. It makes collaboration difficult and decisions end up being all over the place. Some might think that advanced analytics tools can fix this, but in reality, getting everyone on the same page and smoothing out the processes are just as indispensable for making it work.
Data Illiteracy
DDDM isn’t just for data specialists—everyone from C-Suite to line staff should have a fundamental understanding of data and data management basics. Data illiteracy can lead to ineffective communication between data professionals and non-technical stakeholders. It can also hinder the successful implementation of a data-driven culture.
Understanding data and different data management types is necessary in addressing data illiteracy and fostering effective communication across teams, contributing to successful integration of a data-driven culture.
Historical Data Overreliance
Relying too much on the past can also be a stumbling block. It’s like assuming last year’s fashion trends will always be in style—markets change, trends evolve, and decisions based solely on historical data might miss what’s currently happening.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is another significant challenge in data-driven decision-making as it involves favoring information that aligns with pre-existing beliefs or hypotheses while dismissing or downplaying data that contradicts them. Decision-makers may selectively focus on evidence that confirms their expectations, leading to skewed interpretations and reinforcing existing biases.
Poor Communication of Data Insights
Even with accurate data, there can be a breakdown in communication between data analysts and decision-makers, leading to misunderstandings. It’s vital for those involved in data management to communicate findings in a clear, understandable manner, highlighting the relevance of the insights to business objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Companies are Data Driven?
Today, numerous global corporations rely on data for decision-making:
- Google turns to data to drive internal performance by pinpointing the qualities of the most effective managers. This enabled the company to support managers, increase their engagement and performance, and encourage them to stay working for Google.
- Tesla uses big data to drive decision-making, improve vehicle performance, and enhance the overall customer experience.
- Uber uses data, matching algorithms, and prediction models to directly estimate the driving time and allocates the optimal driver through a process.
- Starbucks uses data analytics to know their customers’ preferences and gather details about their purchasing habits.
- Coca-Cola uses data for customer retention and marketing.
What Tools are Used for Data-Driven Decision-Making?
There are many tools and software solutions specifically designed to support DDDM in various industries. These tools let organizations collect, analyze, and visualize data:
- Business intelligence (BI) Tools for data visualization and interactive reporting allow you to create dashboards and analyze data trends.
- Data analytics platforms deliver advanced analytical capabilities, including predictive analytics and machine learning.
- Data warehousing solutions consolidate and store large volumes of structured and unstructured data for smooth data retrieval and analysis.
- Big data platforms handle and process massive volumes of structured and unstructured data for enterprises dealing with large datasets and complex data analytics tasks.
- Machine learning solutions facilitate building and deploying machine learning models that are necessary for predictive analytics and automating decision-making processes.
- Data governance and quality tools ensure data quality, security, and compliance, so your organization can establish and enforce data management policies.
Bottom Line: Data-Driven Decision-Making Is Important
Data-driven decision-making can empower your organization to make informed, objective, and evidence-based choices. It eliminates biases, promoting fair and balanced decisions supported by credible data. By following the steps to data-driven decision-making, your business can establish a systematic and structured process that instills trust in stakeholders and leads to positive outcomes.
Additionally, keep in mind that data management is essential to the success of DDDM, as it guarantees the quality and reliability of your enterprise data. The value of DDDM lies in its ability to transform your decision-making processes, making sure that your business choices are grounded in evidence, analyzed comprehensively, and aligned with organizational goals. If you’re not using data to drive your decisions, you’re missing out on a valuable opportunity to improve your business.
Data management practices are designed to support the effective use of data in decision-making, ensuring that decisions contribute to the achievement of strategic objectives. Read our 10 Best Practices for Effective Data Management article to fully leverage your enterprise data as a strategic asset.



