The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity has fundamentally changed the way businesses protect themselves against cyberthreats. It uses sophisticated machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze enormous volumes of risk data across multiple sources to uncover patterns indicating threats, making it easier to swiftly respond to emerging risks. AI can help you find anomalies and mitigate threats in your IT infrastructure with remarkable speed and accuracy, reinforcing your organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
While the use of AI in cybersecurity is still nascent, it is already showing great promise. Here’s what you need to know to leverage this technology to its full potential.
While useful against known threats, traditional cybersecurity techniques and technologies struggle with the constantly changing nature of cyberthreats. They also rely heavily on manual analysis and known threat databases, limiting their effectiveness. The table below provides a basic comparison that shows how AI-enabled cybersecurity offers advancements in adaptability, response time, and predictive capabilities compared to traditional methods.
| Traditional Cybersecurity | AI Cybersecurity | |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology | Rule-based approaches | Machine learning and AI algorithms |
| Threat Detection | Signature-based detection | Anomaly detection and behavioral analysis |
| Adaptability | Limited adaptability to new threats | Adapts to evolving threats in real-time |
| Response Time | Manual response, slower detection | Automated response, faster detection |
| Human Involvement | Heavy reliance on human intervention | Minimal human intervention through automation |
| False Positives | Higher rates of false positives | Lower false positives through advanced algorithms |
| Predictive Capabilities | Limited predictive capabilities | Enhanced predictive capabilities for proactive defense |
AI addresses the shortcomings of traditional cybersecurity by analyzing massive data volumes, recognizing patterns, and generating insights quickly.
Cybersecurity without AI operates on rule-based methodologies, relying on predefined rules and signatures to detect and block threats. Its threat detection is primarily signature-based, matching incoming data against known attack signatures. This offers limited adaptability to new threats, resulting in slower response times due to manual intervention requirements. Without regularly updating the signature database, cybersecurity solutions might not accurately reflect the current threats, leading to false positives.
Traditional cybersecurity also relies upon human involvement for threat analysis and incident response, which is less efficient and more prone to errors or misses. In addition, traditional cybersecurity tools lack comprehensive predictive capabilities to anticipate future threats effectively.
In contrast, AI-powered cybersecurity uses anomaly detection and behavioral analysis techniques to identify suspicious activities and deviations from normal behavior. AI cybersecurity solutions continuously adapt to evolving threats in real time, delivering automated response mechanisms that accelerate response times and reduce prospective damages.
AI cybersecurity minimizes human intervention through automation, while advanced algorithms contribute to lower false positive rates, increasing threat detection accuracy. Additionally, AI cybersecurity solutions have excellent predictive capabilities, leveraging data analytics to prepare for and take proactive steps against impending threats.
AI has made a substantial impact on cybersecurity by facilitating quick and precise recognition of possible threats, patterns, and irregularities and making it easier to continuously monitor enterprise networks for vulnerabilities and respond to threats as they occur. Combined with this proactive stance toward threat management, AI’s automated incident response reduces the need for human intervention and expedites recovery times.
Using AI to take over routine tasks frees up security professionals to concentrate on more complex aspects of threat detection, malware analysis, vulnerability identification, and incident management. When implemented on a large scale, AI can drastically improve the efficiency of these cybersecurity processes.
It’s worth noting, though, that the development of AI is a double-edged sword. While it strengthens defenses, it also gives malicious actors advanced tools for evasion and targeted attacks. AI can bolster your security defenses, but it can also complicate the threat landscape at the same time—this calls for a consistent cycle of innovation and adaptation in defensive strategies to stay ahead of threats.
Cybersecurity can incorporate AI in many ways, transforming reactive systems to proactive ones. AI helps systems promptly identify and stop potential threats, reducing vulnerabilities. Here are some examples of how AI can be used in cybersecurity:
AI’s capacity for learning, adaptation, and automation has ushered in a new age of detecting and battling cyber threats. It provides several advantages to help you safeguard your entire IT infrastructure against variants of known cyber threats and unknown zero-day threats.
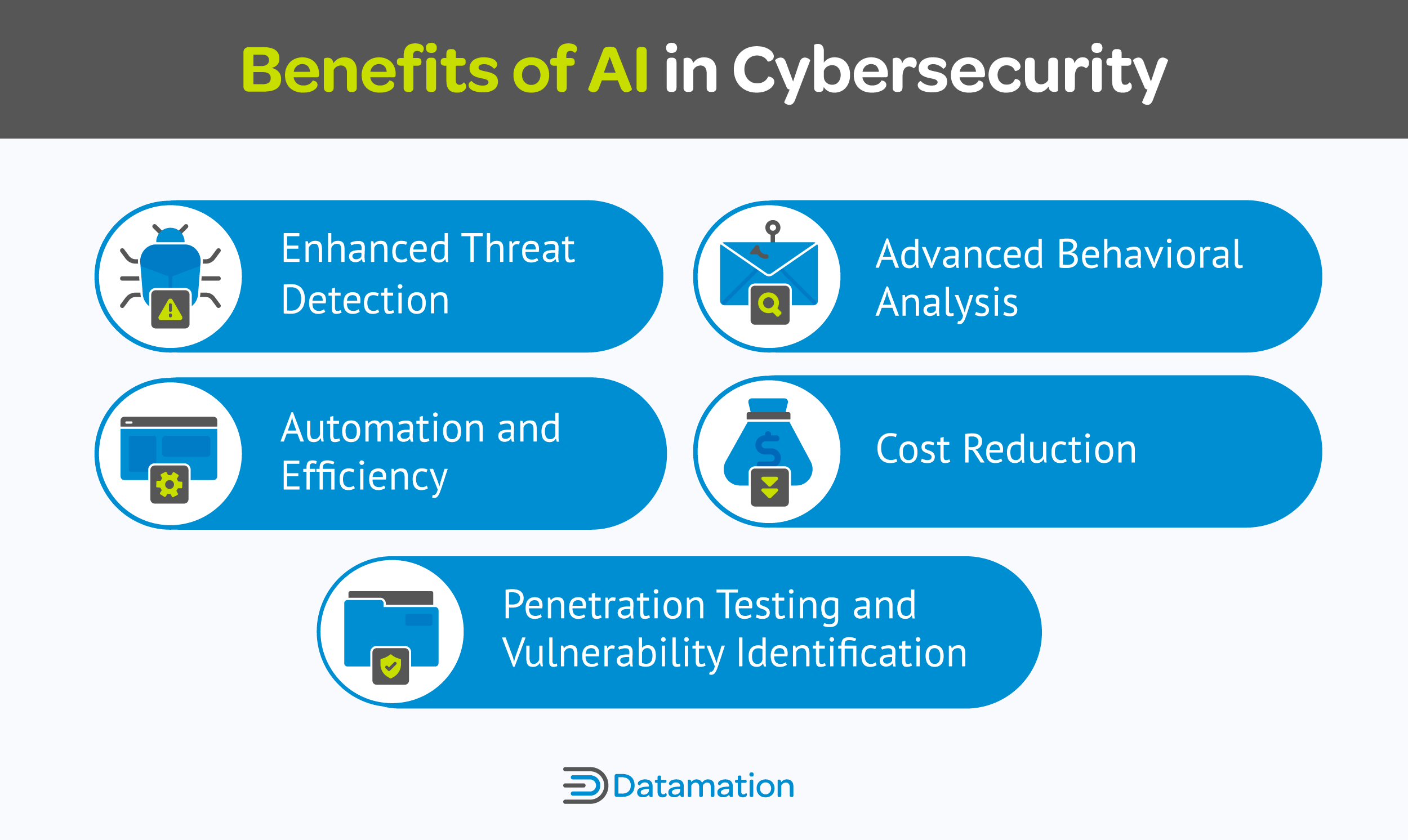
AI speeds up the analysis of vast datasets to pinpoint anomalies, vulnerabilities, and risks that are likely to occur, including advanced threats like polymorphic malware and living-off-the-land (LOTL) attacks. Polymorphic malware is a type of virus that alters its appearance to evade traditional cybersecurity solutions, while LOTL attacks use legitimate tools within the your system to carry out malicious activities. Unlike most traditional cybersecurity tools, AI accurately identifies actual attacks like these, decreasing false positives and prioritizing responses based on real-world risks.
By automating log analysis, vulnerability assessments, and incident responses, AI raises the efficiency of security operations while saving time and resources. It also consolidates reports from multiple data sources, further reducing the costs of cybersecurity operations.
AI monitors, detects, and responds to phishing and social engineering attacks faster than humans can. It also models balance security and user experience by analyzing login attempts and verifying users through behavioral data to prevent fraud.
AI simulates social engineering attacks and penetration testing to expose weaknesses in software and networks before cybercriminals can exploit them. It finds potential risks such as unknown devices, outdated operating systems, and unprotected sensitive data.
AI-driven automation diminishes the need for manual intervention in cybersecurity efforts, resulting in time and resource savings. Additionally, its threat detection accuracy minimizes wasteful resource allocation towards investigating false positives or overlooking genuine security incidents.
While AI offers immense potential in strengthening cybersecurity, it also has its challenges. Understanding and overcoming these obstacles can help you maximize the power of AI in defending your systems, networks, and devices against threats.
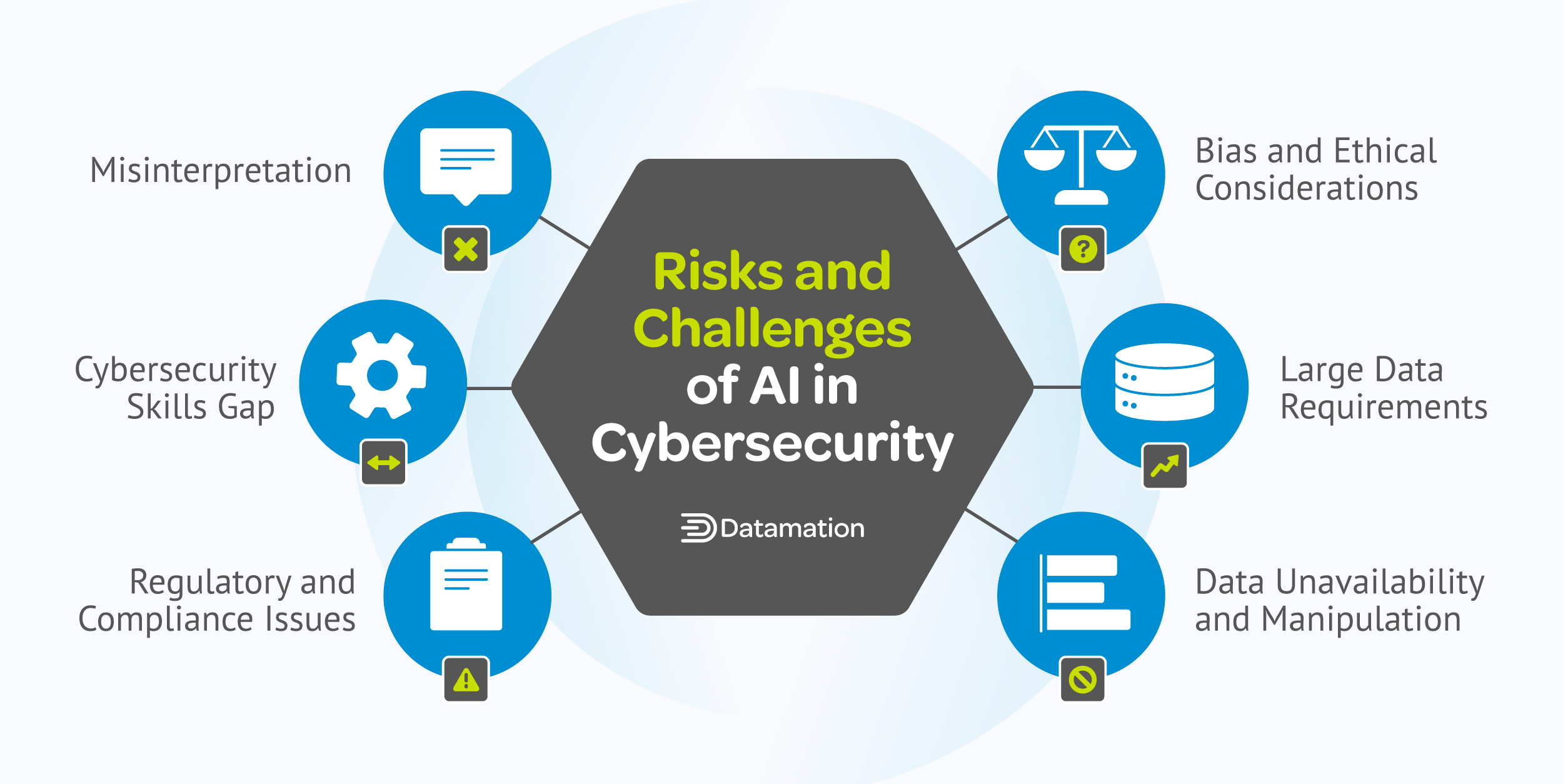
AI algorithms may inherit biases from training data that leads to unfair outcomes or ethical concerns. Dealing with bias is imperative to ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in decision-making processes. Ethical considerations also include concerns about the impact of AI on individual privacy, human autonomy, and the potential for dual-use of AI technologies for malicious purposes.
Since AI systems learn from data and make decisions based on patterns they find in this data, there’s a possibility that they can be tricked by individuals who deliberately put false or biased information into the system, leading to wrong or unfair decisions.
False or incomplete data can cause incorrect threat assessments or AI hallucinations. This could result in real threats being overlooked or false alarms being generated, which in turn might block legitimate operations or restrict authorized users.
Training AI systems to make accurate predictions requires large amounts of data. This poses challenges in data collection, as gathering high-quality and relevant data can be complex and time-consuming.
Integrating AI into cybersecurity introduces a complex set of regulatory and compliance issues. You need a thorough understanding of data protection, privacy, and cybersecurity regulations across different sectors and regions to maintain adherence to these regulations. Staying up-to-date on changes to these laws can also be tricky because they change often.
AI is still a relatively new field, and it’s challenging to find cybersecurity professionals who specialize in this technology. Without these experts, there’s a risk that your AI systems may not be configured correctly, potentially leading to inadequate protection against digital threats.
AI-powered cybersecurity tools help organizations deal with the concerning trend of cybercriminals making use of AI for targeted attacks on organizations. These tools empower IT security teams to minimize risks and enhance the entire enterprise security through automation, machine learning, and predictive analytics. There are a number of reliable cybersecurity solutions using AI on the market, but we recommend three cybersecurity tools in particular for their extensive capabilities.
![]()
Palo Alto Networks’ Prisma SASE is an AI-Powered solution that combines network security, SD-WAN, and Autonomous Digital Experience Management (ADEM) into a single cloud-delivered service.
Visit Palo Alto NetworksThis AI cybersecurity tool secures all apps used by your hybrid workforce, regardless of employee location. Additionally, it protects all application traffic while securing access and data to reduce the risk of a data breach. The AI Operations (AIOps) solution is natively integrated into SASE, allowing IT teams to use AI-based problem detection and predictive analytics to automate complex, manual IT operations, increase productivity, and reduce mean time to resolution (MTTR).
However, Palo Alto Networks’ customer support team takes a while to respond. Configuring and implementing Prisma SASE also requires expertise. Despite these drawbacks, this vendor’s commitment to continuous innovation and Prisma SASE’s best-in-class security make it a worthwhile investment.
![]()
CrowdStrike Falcon platform is a single AI-native cybersecurity solution with threat detection, behavioral analysis, and endpoint protection features. Its AI system is trained on high-fidelity security data and augmented by ground truth from CrowdStrike’s threat hunters, IR experts, and managed detection and response (MDR) services.
Visit CrowdStrikeThe platform’s AI technology can process and analyze data at speed and scale. It recognizes subtle patterns and anomalies that would be imperceptible to the human eye. CrowdStrike Falcon also has built-in predictive capabilities and uses historical data to anticipate and prevent future attacks.
On the downside, this cybersecurity tool is more expensive compared to competitors, particularly because of its range of add-on features that must be purchased separately. But the costs of investing in CrowdStrike Falcon could also be justified by its ability to analyze hyperscale volumes of data.
![]()
The Check Point Infinity Platform is AI-powered and cloud-delivered, providing enterprise-grade security for data centers, networks, cloud tools, branch offices and remote users with unified management. Through AI and automation, it protects enterprises against emerging cyber attacks.
Visit Check PointCheck Point Software employs advanced AI with over 50 technologies to detect and thwart emerging zero-day threats. It recently launched the Infinity AI Copilot, which acts as both an administrative and analytical assistant that automates complex security tasks and gives solutions to security threats.
The platform’s superior AI capabilities that speed up threat detection, mitigation, and response compensate for its outdated documentation. Their customer support team is also available should you need assistance.
AI pattern recognition, prediction, and automated response capabilities hold a big potential in streamlining cybersecurity strategies. However, you must follow best practices for using AI in cybersecurity to make sure you are using the technology responsibly, ethically, and efficiently to protect your digital assets while respecting user privacy. Here are our expert recommendations:
AI is revolutionizing cybersecurity by elevating threat detection, speeding up investigations and automating responses. It enables your organizations to identify potential threats and prevent cyberattacks proactively. AI-powered monitoring also guarantees continuous protection, allowing you to respond swiftly to cybersecurity incidents.
Harnessing AI becomes more necessary each day now that cybercriminals are increasingly using the same technology to develop more sophisticated attacks. But ethical considerations and data privacy must be addressed when implementing AI solutions. Using AI to protect your organization requires careful planning and consideration, but the return is worth the investment because it can lead to significant improvements in cybersecurity.
Get to know the ins and outs of cybersecurity and get certified. Find out our top picks for cybersecurity certifications for 2024 and how they can help advance your career.

Datamation is the leading industry resource for B2B data professionals and technology buyers. Datamation's focus is on providing insight into the latest trends and innovation in AI, data security, big data, and more, along with in-depth product recommendations and comparisons. More than 1.7M users gain insight and guidance from Datamation every year.
Advertise with TechnologyAdvice on Datamation and our other data and technology-focused platforms.
Advertise with Us
Property of TechnologyAdvice.
© 2025 TechnologyAdvice. All Rights Reserved
Advertiser Disclosure: Some of the products that appear on this
site are from companies from which TechnologyAdvice receives
compensation. This compensation may impact how and where products
appear on this site including, for example, the order in which
they appear. TechnologyAdvice does not include all companies
or all types of products available in the marketplace.