The term “big data” refers to both structured and unstructured data in a volume and variety too massive in scale and complexity to be managed using traditional methods. Specialized tools are required to manage the data and to find patterns, track trends, and extract other meaningful information to provide the kind of insights on which businesses increasingly rely. This article explores the pros and cons of working with big data and the challenges it presents and looks at some of the top business intelligence tools to manage it.
Jump to:
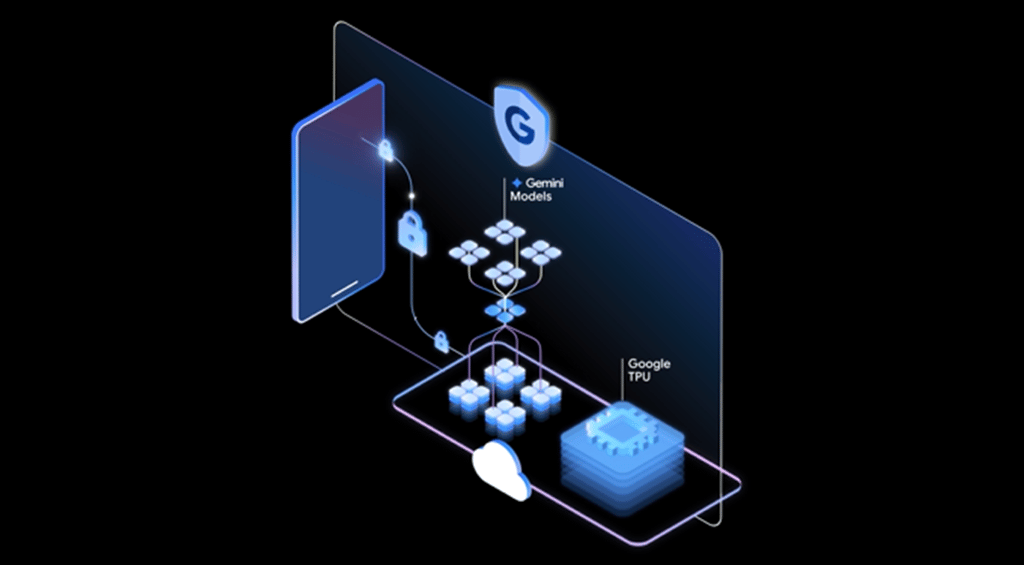
Pros and Cons of Big Data
Big data can give leaders more decision-making resources and insights. It can make enterprise organizations more competitive and help them tailor their offerings to customers with more confidence. It can build customer engagement and loyalty and feed marketing and pricing decisions.
But the vast quantities of information most businesses collect and accumulate can make data management particularly challenging—especially for those organizations not prepared for the task. There are also concerns about what kind of information businesses collect, and what they choose to do with it.
Whether and how a business decides to incorporate a big data strategy into its overall business intelligence efforts will come down to different factors, including goals, budget, and staff, but there are a number of advantages and disadvantages to be considered.
Big Data Advantages
There are many advantages to working with big data, but most fall within a few main categories. Here’s a high-level overview.
Improved Decision-Making Capabilities
Investing in big data can provide the kind of information business leaders need to make challenging decisions, helping them identify and weigh all the relevant factors that can affect the outcome of their choices. Big data can be used across all departments and in all industries.
Historical data, customer data, and competitive market research, for example, can guide businesses when expanding their products and services, moving into new markets or geographic areas, or making acquisitions.
Better Customer Engagement
Meeting customer needs is challenging, especially as companies expand into new markets or offer new products—different customers have varying priorities and interests based on demographics, regional preferences, and more. Big data can provide clarity to help businesses earn customer loyalty and drive sales.
Enterprises can gather data from social media, sales records, customer feedback surveys, and other sources to learn more about their buyers. In fact, data shows that customers reward those efforts—a 2022 study found that 71 percent of respondents expect brands to understand them but less than half felt understood. The strategic use of big data can close that gap.
Increased Opportunities for Social Good
Big data can also provide insights to spark positive, lasting changes—researchers have used it to identify domestic violence and homelessness trends, for example, which can help nonprofits and other organizations provide more appropriate resources and support.
For enterprises looking to expand their corporate social responsibility efforts or highlight their social impact, big data can help them fine tune their resources based on need, interest, and return on investment.
Big Data Disadvantages
Enterprises looking to work with big data will face a number of challenges. Here are the main disadvantages they should consider.
Cost of Doing Business
Big data can be expensive to work with. It’s not as straightforward as investing in a tool and expecting results—working with big data is complex. It requires investments in storage solutions, analytics tools, and cybersecurity and governance programs.
From data scientists and analysts to storage and cybersecurity experts, it also requires staff expertise. Businesses can expect an initial investment and ongoing costs, which might not realize results for some time.
Privacy Concerns
Knowing more about customers can benefit businesses, but it also raises privacy issues. From rewards programs to apps, businesses can gather enormous amounts of information about their customers, their shopping habits and preferences, even their biometric data and their behavior in online and brick-and-mortar stores.
This information can be used to tailor discounts and promotions, but organizations have to walk a line with privacy. A 2023 Razorfish study found that 21 percent of respondents thought brand personalization was simultaneously great and alarming—it also found that half of all respondents would no longer do business with a brand that shared their information without consent.
Data Quality Issues
Even the most advanced big data platforms and cutting-edge technologies can’t compensate for poor quality information. Duplicate records, inaccurate details, and formatting errors are just a few of the many data quality issues and anomalies that can lead to incorrect conclusions.
As businesses gather more information on an ever-expanding scale from disparate sources and try to make it all actionable, it becomes increasingly difficult to ensure consistent quality across the board. Enterprises need to work with experts to audit and validate data on a regular basis.
Talent and Staffing Needs
Working with big data—and big data tools—oftens requires specialized skills. As larger enterprises expand their own data science initiatives, the market becomes more competitive for skilled professionals and smaller businesses begin to struggle to find experienced staff.
Enterprises seeking experienced professionals to work with big data need to invest in their recruiting efforts by offering competitive salaries and benefits and fund education and development for staff if they want to find the right people for critical roles.
Challenges of Working With Big Data
What does it take to establish a big data strategy at the enterprise level? It’s a complex implementation that only succeeds if it has buy-in at all levels of the organization, from line staff to leadership. Shifting to data-driven decision making involves infrastructural investments, data analytics and visualization efforts, software selection and implementation, and ongoing training—in short, it requires a cultural shift.
Here are some of the most common challenges businesses encounter when establishing big data programs:
- Scaling up efforts as needed
- Identifying relevant data types and locations
- Keeping customer data secure and honoring privacy
- Sticking to budgets and timelines
- Getting staff buy-in on new systems, tools, and ways of doing things
- Finding trusted vendors and service providers
Vendors and service providers can help, but they can only do so much. Big data is only helpful if it is used for decision making, and that has to happen within the organization itself.
Business intelligence (BI) tools can facilitate big data efforts by making it easier to manage, analyze, and report on the information to provide the clearest insights. There are a wide range of tools from a wide range of providers on the market, and finding the right one comes down to specific needs. Here are some of the most popular enterprise BI solutions.

Amazon QuickSight
Because so many organizations rely on Amazon Web Services (AWS) for their infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and hosted private cloud needs, Amazon QuickSight has a ready customer base—particularly among those that use the cloud service to store their business data.
It also offers a unique, pay-per-session pricing model that means organizations only pay for their use of interactive dashboards. Other key features include scalability, the SPICE in-memory calculation engine, ML Insights, embedded analytics, and a mobile interface.

The Cloudera Data Platform is a hybrid tool marketed to businesses with information spread across public and private clouds or on-premise facilities. User-friendly dashboards and enterprise-grade data security and governance features help company representatives use customer information in trustworthy, responsible ways.
Microsoft Power BI
Microsoft’s Power BI is a popular tool that lets users create a single source for all data, promoting easy access and analysis. It includes many options for visualizations to make it easier to work with data across stakeholders and teams.
Power BI gets strong reviews from analysts and is one of the best-selling business intelligence tools. Noteworthy features include advanced data protection and governance capabilities, integration with other Microsoft applications and cloud computing services, self-service analytics, fast data preparation, streaming dashboards and more.

Qlik Sense
Qlik’s flagship BI software, Qlik Sense, incorporates an artificial intelligence-based associative analytics engine. Other features include fast performance, insight suggestions, automation, mobility, open APIs, and multi-cloud deployment options.
Qlik’s AI and augmented intelligence capabilities differentiate it from many of the other BI applications.
The company is focused on making analytics accessible to all, and accordingly, its platform is very user-friendly. Multi-cloud support gives enterprises a lot of flexibility in deployment.

Tableau
Tableau is an all-purpose data management tool that allows people to prepare, evaluate, and share information. Acquired by Salesforce in 2019, Tableau continues to sell its BI software under its own brand name and includes a wide variety of elements, including Desktop, Browser, Mobile, and Embedded versions. It incorporates data preparation, governance, content discovery, analytics, and collaboration capabilities, and can be deployed in the cloud or on premises.
While the price tag can be high depending upon the implementation, Tableau offers very powerful data visualization capabilities and creates attractive dashboards. It also has an extensive library of online help and active public support forums.
Read Best Business Intelligence Software and Tools to learn more about what differentiates the best BI platforms on the market and they meet your needs.
Bottom Line: Using Big Data for Good
Big data can be a game-changer for enterprises looking to step up their business intelligence programs. When done well, big data can provide insights about customers, fuel data-driven decision-making, and feed many aspects of businesses’ work, from marketing to finance to human resources. But working with big data requires investments in infrastructure and staff, corporate cultural shifts, and an expertise-driven strategy.
It also demands careful attention to privacy rights and security concerns. Companies working with big data need to find a balance in how they use what they know about their customers. Big data can help them improve promotions, better target advertising and marketing campaigns, and highlight products that cater to their preferences—but it can also be used in troubling ways, both by intent and by carelessness.
By being transparent about what data they collect and what they plan to do with it and being explicit about the perks of providing data, businesses can boost customer engagement and brand loyalty while making their customers feel valued rather than exploited.
To see how the most popular tools for analyzing and visualizing data stack up again big data needs, read Top 7 Data Analytics Tools and Software in 2023.