Datamation content and product recommendations are
editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links
to our partners.
Learn More
As members of a highly regulated industry, healthcare organizations have moved into cloud computing carefully. Nevertheless, IDC estimated that healthcare organizations would invest $13.6 billion in cloud technologies between 2018 and 2019 – a hefty increase over the prior period.
In the healthcare industry, there is considerable concern for the protection of personally identifiable information (PII) since healthcare records include the patient’s name, address, social security number and medical history. If that information is abused or misused, a healthcare company could face private actions, class actions and regulatory fines. In a cloud computing context, machine learning or data analytics is applied to the data, though cloud computing and cloud storage tend to go together for efficiency purposes.
Cloud Storage and Backup Benefits
Protecting your company’s data is critical. Cloud storage with automated backup is scalable, flexible and provides peace of mind. Cobalt Iron’s enterprise-grade backup and recovery solution is known for its hands-free automation and reliability, at a lower cost. Cloud backup that just works.
SCHEDULE FREE CONSULT/DEMO
Over the years, the healthcare industry has been undergoing digital transformation, as Big Data and healthcare grow increasingly intertwined. As part of the transformation, paper healthcare records are being replaced (and have largely been replaced) by electronic healthcare records, or EHRs. Sometimes those records are anonymized for research purposes, such as to determine the leading factors leading to hospital readmission.
Many healthcare organizations take advantage of cloud computing for research purposes, whether working on gene sequencing, the molecular structure of a new drug or determining disease patterns. Using cloud resources, they are able to achieve more in shorter time frames and at lower costs than using traditional computing resources. More recently, researchers are also taking advantage of the machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities cloud computing providers offer, which is contributing to new discoveries.
Also see: Top Cloud Computing Companies
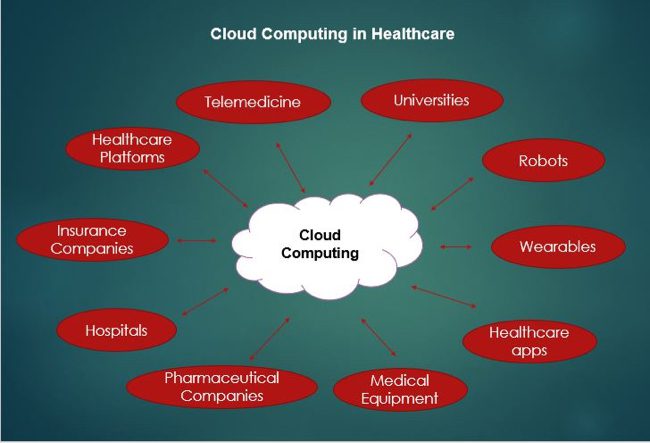
Examples: How Healthcare Providers Use the Cloud
Healthcare organizations use cloud computing in myriad ways. Several Amazon Web Services customers are a good example:
- 3M uses cloud to provision compute resources faster, deploy software faster and analyze the total cost, quality and outcomes for patients and populations.
- Global pharmaceutical company Allergan runs 400 product websites and marketing applications in the cloud.
- Medical imagining solution provider Arterys can render multidimensional models of the heart in 10 minutes versus the industry standard of 90 minutes.
- Pharmaceutical company Bristol-Meyers Squibb is able to run clinical trial simulations 98% faster than in its previous environment.
- The DC Health Benefit Exchange Authority is able to instantly deploy software that enables enrollment-as-a-service solutions for healthcare customers. It’s saving $1.8 million annually.
- NexGen Healthcare runs its mission-critical applications in the cloud.
- Health information exchange and healthcare integration solution provider Orion Health used the cloud to scale its platform which is now capable of handling millions of patient records.
- Biotechnology company Sequence Bio uses cloud to compete genetic data and to help identify patterns across disease and genetic groups.
- UC Santa Cruz Genomics Institute processes 20,000 cancer samples in days instead of months, saving hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- Governance, risk and compliance platform provider Verge Health shortened the time to deploy Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)-compliant development environments from three weeks to a few minutes.
Benefits and Advantages
- Scalability/Flexibility. Cloud computing resources can be dynamically scaled as necessary to meet compute needs. The rise of medical and healthcare IoT devices can dramatically increase the amount of data a healthcare company handles. As the amount of data and data types grow, so does the associated complexity of what can be analyzed and the number of possible correlations.
- Capacity. Cloud computing capacity rivals supercomputers, albeit at a lower cost.
- Collaboration. Pharmaceutical companies, universities and other researchers use cloud computing to facilitate more effective and timely collaboration.
- AI and Machine Learning. Large cloud providers offer AI and machine learning capabilities that enable healthcare companies to learn more about patients and populations. Some types of machine learning, specifically, unsupervised learning and deep learning, are able to identify patterns that humans have not previously identified.
- Security and Compliance. The largest cloud providers including Amazon AWS and Microsoft Azure invest more in security than any one company is capable of doing for itself. Some security is provided in basic services, though organizations in the healthcare industry tend to need additional security and HIPAA compliance to meet their needs which the major cloud providers offer.
- Reliability. Cloud environments are redundant so if one location fails, another can take its place. This results in minimal data loss and compute disruption (which can be a major time and cost factor when solving a very difficult, data-intensive problem).
- Real-time Data. As the healthcare industry has become more digital, its ability to process information has accelerated. Rather than tracking patient data in batch format, organizations are increasingly monitoring patients in real-time so they can affect intervention faster which improves patient health outcomes and can help lower the overall cost of the patient’s healthcare.
- Cost. Cloud computing costs are far cheaper than supercomputers.
- Latest Technology. Cloud computing providers invest in the latest technology to stay competitive. Companies relying on their own resources must amortize the cost of existing resources and only invest in new technology as strategically and financially prudent for their own use.
- Faster and More Cost-Efficient Research. Cloud computing environments can analyze huge amounts of data using massively parallel compute resources. The result is faster research results at significantly lower costs.
- Architectural Flexibility. Healthcare organizations can add cloud computing resources to improve the ROI of workloads across their architecture.
Challenges and Issues
- HIPAA Compliance. The major cloud providers offer healthcare cloud solutions that include HIPAA compliance. Smaller cloud providers may not do the same.
- GDPR Compliance. Many top cloud providers comply with the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Microsoft, for instance, provides GDPR compliance tools for Azure.
- Implementation. Moving compute workloads to the cloud requires knowledge of how the different in-house data center and cloud environments differ and how that changes the company’s cost and risk profile.
- Security. Although the major cloud providers provide robust security services, it is possible to misconfigure a cloud-based resource in a manner that exposes sensitive data. Also, no solution, cloud or otherwise, is absolutely secure since hackers are always innovating.
- Outages. Cloud computing environments experience outages despite their inherent redundancy. This factor should be considered when calculating the total cost of cloud computing vs. the total cost of other options. To do that, healthcare companies need to understand the details of cloud options.
- Data Ownership and Handling. Getting data into a cloud is easy, getting it out isn’t always so easy. In addition, HIPAA gives patients the right to know who has handled their data. These risks must be considered and cloud service provider contracts reviewed in fine detail to ensure a healthcare organization doesn’t expose itself to these risks.
Future of Healthcare and the Cloud
As cloud computing technology innovation continues to accelerate, changing healthcare practices and IT along with it. The following are a few emerging scenarios and their likely impact on healthcare IT.
Machine Learning
The major cloud providers provide machine learning capabilities that can rapidly advance customers’ capabilities. Although businesses now understand the connection between data quality and useful analytics, the same understanding is not necessarily true for data and machine learning. Bad quality data makes for bad quality machine learning training data. Bad quality training data results in erroneous machine learning. IT will also have to become more sensitive to the various types of unintended bias that can creep in, since bias can impact the rights of individuals in very personal ways.
Robotics
Robots are finding their way into hospitals and elderly care facilities. Cloud computing providers are making it easier to design and build robots, which will mean more developers working in IT departments will be able to build robots that previously would have required knowledge they didn’t possess. Since a robot is an Internet of Things (IoT) device, it uses the cloud to help process information, so security and privacy need to be considered. The use of digital twins (a digital replica of an physical asset) helps increase the reliability of IoT and other devices by comparing their ideal state to their current state. However, should robots malfunction or fail, IT would be called in to help troubleshoot and resolve the issue.
Nudging
AI systems, whether software or embedded (such as in robots) are used by marketers and other parties to change the behavior of people. In a healthcare setting, the obvious use is to help patients make healthier lifestyle choices. However, the same technology can be used to affect the opposite if hacked or designed to do so. That means an AI or a robot could be programmed or reprogrammed to encourage unhealthy lifestyle choices. Similarly, if misused, they could amplify mental health issues. IT should understand the risks.
Security
More healthcare-related IoT devices and wearables are becoming part of the modern healthcare IT fabric. Therefore, chief information security officers (CISOs) will need to be able to identify vulnerabilities, assess the threat landscape and prioritize the vulnerabilities that are most likely to be exploited – including those in the cloud. Because this task continues to become more complex with more devices, software, and hardware, IT and security teams need the right tools in place to manage security risks.
Data Enhancement
Healthcare organizations, like other organizations, will increasingly want to use third-party data to supplement what they already have in place to perform more advanced forms of analysis. The additional data provides additional context, such as weather patterns that result in disease outbreaks, locations in which disease outbreaks are more likely to happen, etc. Given HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulations, it’s important that data-related innovation doesn’t expose a healthcare organization to unnecessary risks.
Voice Interfaces
More types of devices and medical equipment will become voice-controlled and they will use the cloud for backend processing. However, voice technology is still improving – it’s far from perfect. IT needs to understand how voice interfaces perform and what their limitations are, so they can troubleshoot and help provides solutions. In some cases this may require defaulting to a given language, based on the needs of a multilingual audience.
Telemedicine
Already cloud-based telemedicine is being provided to individuals living in the remote areas of developing countries, so those communities can have some type of access to healthcare. For example, a community representative can take a picture using a tablet, which is analyzed and diagnosed using an AI instance or a human healthcare provider. In developed countries, telemedicine enables an extension of services, such as psychiatric care to a patient who is unable to travel. Regardless of how telemedicine platforms and apps are designed, their back ends tend to process information using extensive cloud computing resources. Telemedicine, like video conferencing, can be disrupted by network noise or bandwidth issues. Since the failure is technology-related, IT is the go-to source for troubleshooting and resolution.
SEE ALL
CLOUD ARTICLES